night vision goggles military
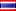
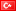
Military night vision goggles are a crucial piece of military equipment that utilizes photoelectric conversion to assist soldiers in concealed observation at night or in low-light environments. The following provides more information:
Classification and Features
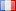
Low-light-level night vision goggles: These directly utilize weak nighttime skylight, such as moonlight, starlight, and atmospheric glow, to illuminate the target. An image intensifier converts the reflected radiation from the target into an enhanced optical image. While their concealment is excellent, they are significantly affected by natural lighting conditions and are susceptible to camouflage and interference.
Low-light-level night vision goggles
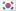
Active infrared night vision goggles: These combine image intensification technology with an active illumination source in the near-infrared or short-wave infrared bands. The goggles emit an infrared beam, illuminating the target and converting the reflected infrared image into a visible light image. They are not limited by illumination and offer excellent observation in complete darkness. However, their observation range is short, and the infrared light they emit can be easily detected by enemy night vision goggles, thus exposing the target. Therefore, they are rarely used in military settings.
Active Infrared Night Vision Goggles
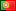
Passive Infrared Night Vision Goggles (thermal imagers): These display images based on the temperature difference between the target and the background. They can detect and identify targets that are typically camouflaged, allowing for covert observation both day and night. They have high anti-interference capabilities, but their range is significantly affected by weather conditions and are expensive.
Development Trends of Passive Infrared Night Vision Goggles
Balancing Panoramic Viewing and Lightweighting: Four-lens night vision goggles achieve a panoramic field of view exceeding 120° through multi-lens stitching. They also utilize a carbon fiber casing and low-power chips to keep the weight under 600 grams, improving wearer comfort and observation quality.
Deep Integration with Individual Soldier Systems: In the future, these goggles will be further integrated into the "Individual Soldier Integrated Combat System," linking with helmet-mounted displays and voice command systems. For example, navigation arrows and friendly force location markers can be overlaid on the night vision goggle screen. They can even share the same view with the scope of a smart rifle, enabling "see, aim" functionality. Breakthrough in low-light, full-color imaging: Developing a new generation of low-light CMOS sensors enables full-color imaging in extremely low light conditions, such as 0.001 lux (equivalent to a moonless night), replacing traditional black-and-white night vision images and improving target detail recognition.